
Installing your own Git server
In-House
Git [1] is a peer-to-peer system, so you don't really need a server, but if you are developing software or working on other files in a team, a central file repository that you can back up is a good idea.
A web service would do the same job, such as Gitorious [2] or the omnipresent GitHub [3], which is free for open source projects. The commercial service by GitHub starts at US$ 25 a month, ranging up to US$ 200 for the Platinum service, whereas Gitorious [4] costs at least US$ 99 for your own sub-domain.
When installing your own Git server, you can take several approaches. The two most popular are Gitolite [5] and Gitosis [6]. Both are available from GitHub. Gitolite is written in Perl and Gitosis in Python, but otherwise they are pretty similar. Many distributions (such as Fedora and Ubuntu) include the two programs in their package repositories, which makes the install very easy. The two tools use different installation approaches, thus leading to different configuration steps.
The basic requirements for setting up a Git server are a directory for the configuration and the repositories, a user account, and SSH keys needed to handle authentication. Access to Git repositories always relies on SSH, which means the Git servers don't need a separate port. Theoretically, you could install Gitosis parallel to Gitolite, but with a separate user ID in each case.
Gitolite
On Ubuntu, Gitolite installs the package, but does not set up the user or the directory. On Fedora, when you complete the package install, you have a gitolite user and a /var/lib/gitolite directory for the repositories. Here, I will describe how to install manually with a user account named git and home directory /home/git. Figure 1 shows the principles of the installation and use.
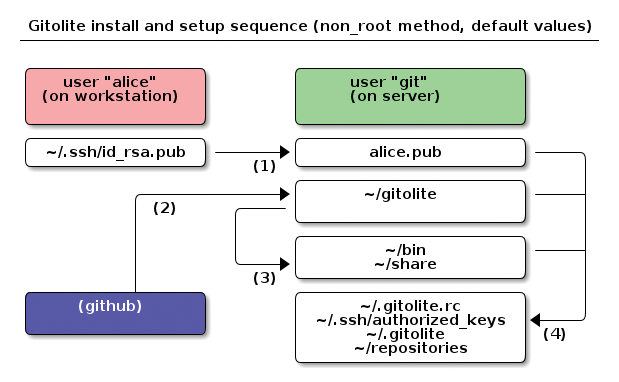
As the future Git server administrator, you need to copy your public SSH key (from a workstation/client computer) to the server and deposit it in a directory the git user account can access (e.g., the tmp directory):
scp .ssh/id_dsa.pub Server:/tmp/ofrommel.pub
If you don't have a keypair, you can run ssh-keygen to create one. On the Git server, you first need to download the software from GitHub:
git clone git://github.com/sitaramc/gitolite
Still working as root, run the install script, which installs the Gitolite programs globally:
# gitolite/src/gl-system-install using default values for EUID=0: /usr/local/bin /var/gitolite/conf /var/gitolite/hooks
You can also do this as the Git user, but then all of the files will end up in that user's home directory. Next, you can change your user ID by typing su - git and then import your SSH public key into Gitolite:
gl-setup /tmp/ofrommel.pub
Gitosis shows you the /home/git/.gitolite.rc configuration file again; normally, you will be able to keep the defaults. On the client computer, you can now clone the repository that Gitolite includes for administration. Management tasks proceed as follows in future: edit the configuration locally, then upload the changes to the server. The following command clones the repository:
git clone git@192.168.111.20:gitolite-admin.git
If the connection fails, the SSH configuration might be at fault. The Git user's .ssh/authorized_keys file must look something like Listing 1. The important part is the command= line.
Listing 1: .ssh/authorized_keys
01 # gitolite start 02 command="/usr/local/bin/gl-auth-command ofrommel",no-port-forwarding,no-X11-forwarding,no-agent-forwarding,no-pty ssh-dss AAAAB3NzaC1kc3MAAACBAOvwG6F0D2v2J8d+RsQFwozOqqFAgGkMfDK86TUA 04 ... 05 # gitolite end
If everything worked, you will have a new directory, gitolite-admin, with two directories named conf and keydir. Next, edit conf/gitolite.conf to create a new repository. By default, it will contain a test repository:
repo gitolite-admin
RW+ = ofrommel
repo testing
RW+ = @all
As you can see, only the ofrommel user account (key owner) has read and write access to the gitolite-admin repository. To create a new repository, you can copy the testing entry (both lines) and modify its content. Then, confirm the changes by entering git commit -a. The git push command uploads the changes to the server, which confirms that a new repository has been created:
Initialized empty Git repository in /home/git/repositories/project.git/
You need to add the public keys of the other Git users (with matching file names) in the keydir subdirectory and commit and push the changes as described above. For more information – for example on the syntax – go to the $HOME/share/gitolite/conf/example.conf file on the Git server or the /var/gitolite/conf/example.conf file, or surf to the exhaustive Gitolite wiki [7].
Gitosis
Gitosis works basically the same way as Gitolite: You need a special user account with an SSH configuration to call the corresponding scripts. If you install Gitosis on Ubuntu, you will find that you have a gitosis user account and a /srv/gitosis directory on completion. In a similar style to Gitolite, Fedora also creates a /var/lib/gitosis directory for Gitosis with a user account to match. Again, I'll demonstrate a manual install to clarify the approach.
To begin, check out the Gitosis software from the GitHub repository in the administrator's home directory, /root:
git clone git://eagain.net/gitosis.git
Still working as root, change to the Gitosis directory and run
python setup.py install
to install the files globally. Then, copy your public key to the server as described in the section on Gitolite, change user (su - git), and continue working with the Git user ID; install Gitosis with the key:
gitosis-init < /tmp/ofrommel.pub Initialized empty Git repository in /home/git/repositories/gitosis-admin.git/ Reinitialized existing Git repository in /home/git/repositories/gitosis-admin.git/
If you see an error message complaining about missing permissions, you might have checked out the Gitosis distribution in root's home directory, which you are not allowed to overwrite as git.
As with Gitolite, administration in Gitosis uses a special repository. You can check it out on your client as follows:
git clone git@192.168.111.20:gitosis-admin.git
The gitosis-admin directory now contains the gitosis.conf configuration file and the keydir directory for the SSH keys. The configuration, to which a webcoders group and a new webproject repository have been added, is shown in Listing 2. Then, do a git commit -a and git push to send the changes to the Git server.
Listing 2: gitosis.conf
01 [gitosis] 02 03 [group gitosis-admin] 04 members = ofrommel@admin-magazin.de 05 writable = gitosis-admin 06 07 [group webcoders] 08 members = ofrommel@riker.linux-magazin.de 09 writable = webproject
To create the new project, create a new directory named webproject and change to the directory. Then, run the following two commands to initialize the repository:
git init git remote add origin git@192.168.111.20:webproject.git
After adding new files to the directory, you can subject them to version management with git add. To synchronize the repository with the server for all branches, again run the push command:
git push origin master:refs/heads/master
If an error occurs using Gitosis, you can enable debug messages by opening the gitosis.conf configuration file, looking for the [gitosis] line, inserting a line that reads loglevel = DEBUG, and then pushing the results to the server in the normal way.
For more information on the use of Git, check out a previous Linux Magazine article [8] or the Pro Git [9] book, which is available free of charge online and contains a chapter each for Gitosis and Gitolite.
If you would like to get a view of the repositories in your web browser, you can use Gitweb as your web front end, although it definitely does not give you the good looks of GitHub's front end.
