Tools for incident response and memory analysis
Memory Check
Protecting your network environment with the latest virus protection, controlling what software is installed and allowed to run, restricting network access, protecting web browsing, limiting user account access, updating security patches … . All these efforts are critical, but all will fall short if you don't have the proper monitoring to detect villainy on your network and respond quickly. When your network has the proper monitoring in place, and knowledgeable engineers are monitoring for outbreaks, you will have a better view of how traffic flows in your environment. When you understand how traffic flows, you can respond better when something bad happens.
Incident response involves addressing and managing the security events on a network and providing a proper response to those events. The end game is to limit the damage and reduce recovery time and costs. The best way to achieve these goals is with an incident response plan that includes a step-by-step process that investigators should follow when an attack has taken place.
One important step for in the investigation process is to analyze the memory of the infected computer. A well-designed computer intrusion investigation is not limited to data on disk: Evidence is collected from additional data sources, including network traffic and volatile memory. This paper describes procedures for making an accurate and reliable copy of volatile memory content so that the investigator can examine the data for further evidence. Looking directly at memory can turn up clues that might be hidden in a view of the disk. For instance, a trojaned version of the ps command might not report the presence of a malware process running on the system, but a close look at memory reveals the presence of that hidden process.
The only way to get a perfect and undisturbed view of memory is to capture a snapshot of memory to an image file and then extract that file to another system for viewing. This process requires several steps, and it is a good idea to have all the necessary tools ready in advance, so if an incident occurs, you'll be in position to start your investigation before the attack spreads to other systems.
In this article, I focus on the following tools:
- F-Response TACTICAL [1] – a tool used to create a secure connection between the infected computer and the computer you will use as the examining system. TACTICAL, which comes in the form of two USB sticks, is designed to streamline live analysis, collection, and authentication. When used correctly, this tool provides direct, live, read-only access to the remote target computer's disks, volumes, and physical memory. An executable runs directly from the provided USB storage. No software is installed on the target computer. F-Response TACTICAL works with all RAID disks, physical drives, logical volumes, and physical memory (32- and 64-bit windows).
- dc3dd [2] – a tool that captures the content of memory on the infected system;
dc3ddis basically the standard *nixddutility upgraded for forensic use, which allows you to take hashes and split an image, all from one command. - Volatility [3] and Mandiant Redline [4] – free tools used to analyze the memory image file.
I'll describe how these tools work together to capture, transfer, and analyze a memory image file. In this case, the analysis turns up some hidden processes running on the infected system. Volatility and Mandiant Redline are very versatile tools capable of discovering many other kinds of clues. In a later article, I will take a deeper look at memory analysis with Volatility and Mandiant Redline.
TACTICAL: Connecting to the Infected System
In this section, I show you how to investigate a malware-infected Windows system using a Linux-based examiner platform to acquire the image.
F-Response TACTICAL is a simple and inexpensive tool that helps you gather an image file from an infected computer. The TACTICAL solution requires only two USB sticks. One USB stick, labeled TACTICAL Subject, goes on the infected computer. The other stick, labeled TACTICAL Examiner, goes on another computer on the network that you will use as the platform for launching and monitoring the investigation.
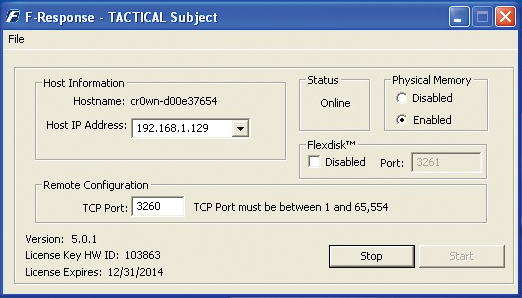
Once the USB stick is loaded on the Windows system, start the program so it can listen on its external interface (see Figure 1). Because the tools run from the USB stick, you don't have to install any software, which means the intruder won't see any evidence of its presence on the system.
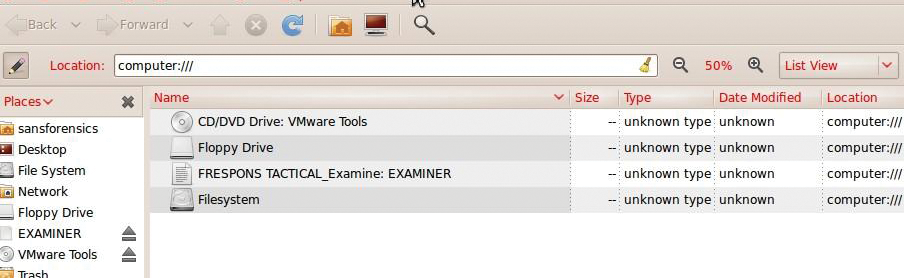
On the examiner platform, insert the Examiner USB stick and make sure it shows up as loaded (Figure 2). Next, start the executable on the F-RESPONSE Examiner USB stick (Figure 3),
$ ./f-response-tacex-lin.exe -s 192.168.1.129 -p 3260
specifying that the target Windows computer with the Subject USB stick is at 192.168.1.129 and listening on port 3260. The system connects to targets
iqn.2008-02.com.f-response.cr0wn-d00e37654:disk-0iqn.2008-02.com.f-response.cr0wn-d00e37654:disk-1iqn.2008-02.com.f-response.cr0wn-d00e37654:vol-ciqn.2008-02.com.f-response.cr0wn-d00e37654:vol-eiqn.2008-02.com.f-response.cr0wn-d00e37654:pmem
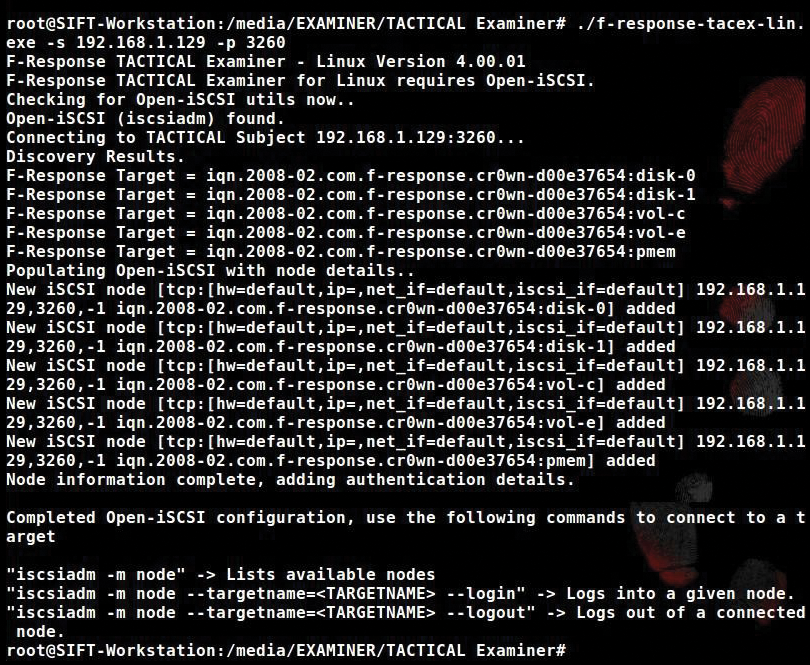
In this case, I am looking for the running memory (pmem) on the target computer, so I can ignore disk and vol targets.
Next, log in to iqn.2008-02.com.f-response.cr0wn-d00e37654:disk-0 with the command (Figure 4):
# iscsiadm -m node -targetname=iqn.2008-02.com.f-response.cr0wn-d00e37654:disk-0 --login
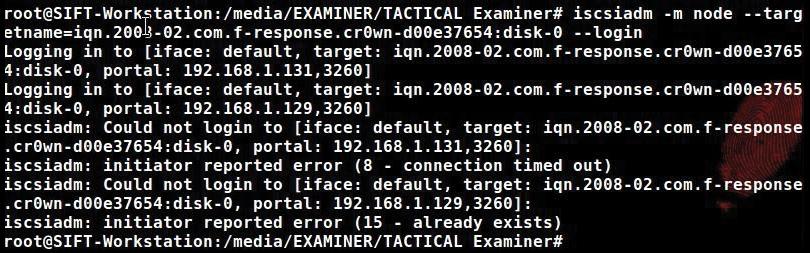
The iscsiadm command is an open-iscsi administration utility that allows discovery and login to iSCSI targets, as well as access and management of the open-iscsi database. The -m option specifies the mode, which is node in this case.
The mode could also be defined as: discoverydb, fw, host iface, or session. With the mode selected as node, use the -targetname= parameter to specify the location of the target drive. After successfully connecting to the remote machine, run fdisk -l and see the new device located at /dev/sdd1 (see Figure 5).
When the login command completes, you can mount the device nodes to your machine locally for analysis using the mount command. Next, mount the partition /dev/sdd1 with the command:
# mount -o ro,show_sys_files,streams_interface=windows /dev/sdd1 /mnt/windows_mount
Using mount with the option -o ro will mount the filesystem read-only, show_sys_files shows all system files as normal files, and streams_interface=windows controls how named data streams in WIM files are made available with windows as the named data stream. This command will mount the memory from the Windows system to /mnt/windows_mount. After changing into that directory and listing the files, you will see the list of files followed by a login to the pmem location (Figure 6).
The pmem location is where the memory (RAM) resides on the target. I have made a forensic image of that memory and placed it on the examining computer for analysis.
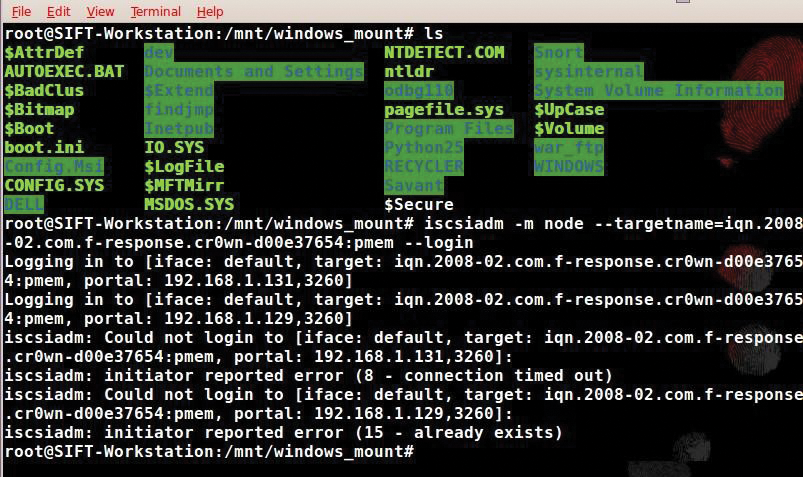
Now I need to log in to the process memory of the target system, which is the pmem location. I will use the iscsiadm open-iscsi administration utility to perform this task with the following command:
# iscsiadm -m node -targetname=iqn.2008-02.com.f-response.cr0wn-d00e37654:pmem -login
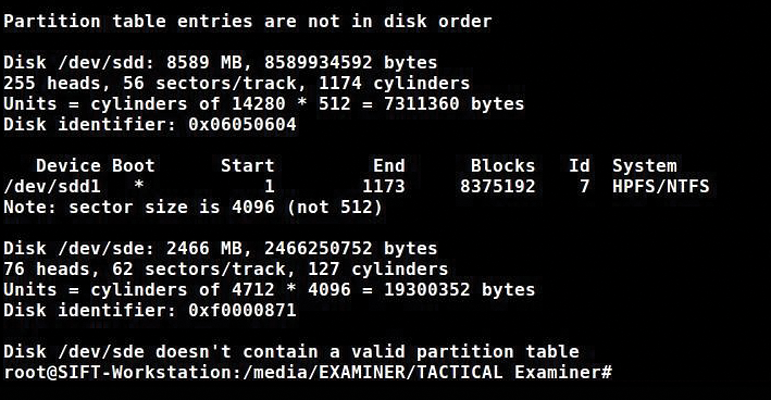
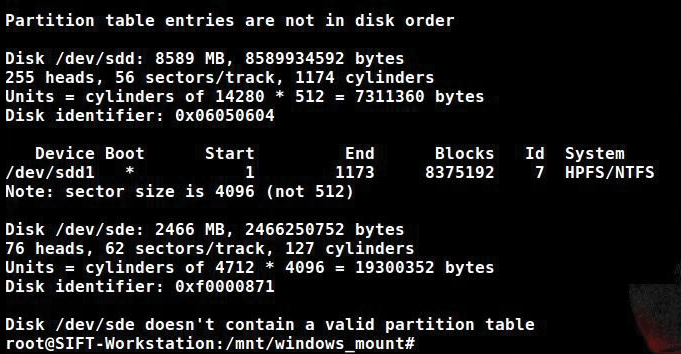
Again, I will use the isciadm utility and the node option with -targetname to specify the location of pmem. Now I run fdisk -l and see the partition tables (Figure 7).
Imaging Memory with dc3dd
I can image the remote system's memory with the use of dc3dd, which was developed by Jesse Komblum at the DoD Cyber Crime Center. Dc3dd is similar to dd but is designed for forensic work, allowing you to take hashes and split an image all from one command. Taking hashes in a forensic examination ensures authenticity of the file – in this case, the memory image. The ability to split an image into workable, fixed-size chunks is also an advantage.
Open up a terminal and type:
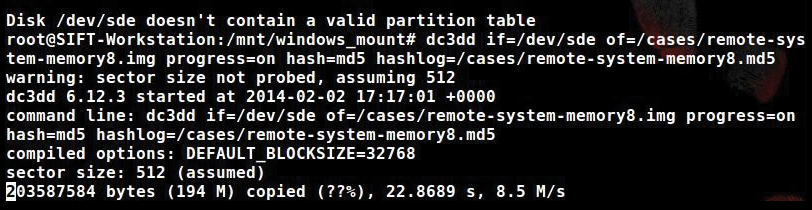
# dc3dd if=/dev/sde of=/cases/remote-system-memory8.img progress=on hash=md5 hashlog= /cases/remote-system-memory8.md5
The command breaks down as:
-
if=DEVICEorFILE– Read input from a device or a file, in this case/dev/sde -
of=FILEorDEVICE– Write output to a file or device, in this case/cases/remote-system-memory8.img -
progress=on– Show progress on-screen -
hash=ALGORITHM– Compute a hash of the input and also of any outputs (specified usinghof=,hofs=,phod=, orfhod=.ALGORITHMoptions includemd5, sha1, sha256, orsha512. -
hashlog=FILE– Log total hashes and piecewise hashes toFILE.
This command does a forensic copy of the Windows memory file to your computer; you can see a screenshot of the progress in Figure 8. (A forensic copy is a copy that shows the hash, therefore proving authenticity.)
Analyzing with Volatility
Now that I have an image file of the Windows memory, I can analyze the file for the existence of malware. Several tools are available for this task, including Redline by Mandiant. An important open source analysis tool is Volatility, implemented in Python for the extraction of digital artifacts from volatile memory (RAM) samples.
If the memory image was acquired from an unknown system, you can use Volatility to identify the operation system (Figure 9).
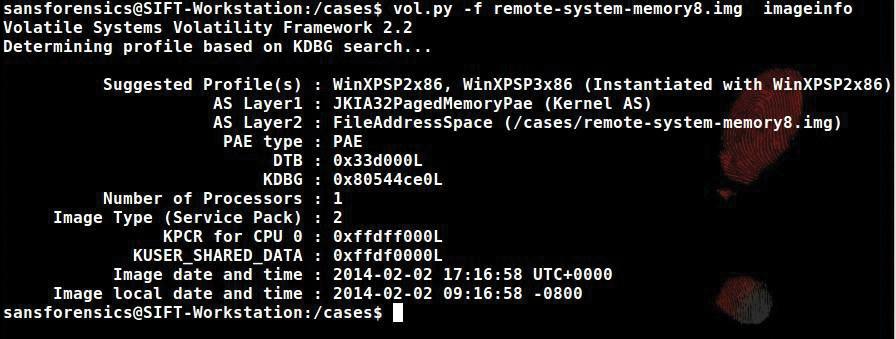
Volatility's imageinfo plug-in finds the operating system to which the memory dump belongs. In Figure 9, the suggested profile portion of the output shows a WinXP SP2x86 system; you will need this information to perform more work on this memory image file.
To look at the running processes, use:
$ vol.py -profile=WinXPSP2x86 pslist -f remote-system-memory8.img
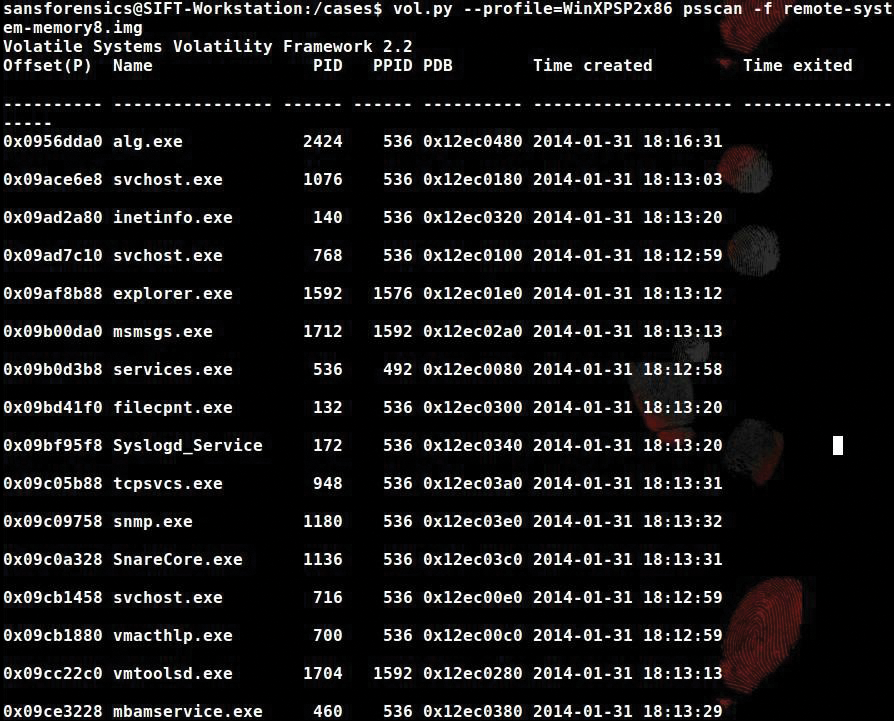
You can use the psscan plugin to scan the memory image for EPROCESS blocks with the command:
$ vol.py -profile=WinXPSP2x86 psscan -f remote-system-memory8.img
Use psscan to enumerate processes using pool tag scanning, which finds processes that have terminated and that have been hidden or unlinked by a rootkit (Figure 10).
Looking for Processes with Redline
The Mandiant Redline application is another option for analyzing the memory image file. To use Redline, copy the Windows memory images off the Examiner system to a separate Windows workstation, where the Mandiant Redline application is installed.
Mandiant Redline (Figure 11) is a free tool that provides host investigative capabilities to users and uncovers signs of malicious activity through memory and file analysis to develop a threat assessment profile. After I infected the test Windows box with a known malware variant and allowed the system to react, the machine wanted to restart at that moment. I acquired a memory image and loaded it into Redline. I then allowed the machine to reboot and took another memory image. All the processes that are running on the system are in Figure 12 (left, before reboot, and right, after reboot).
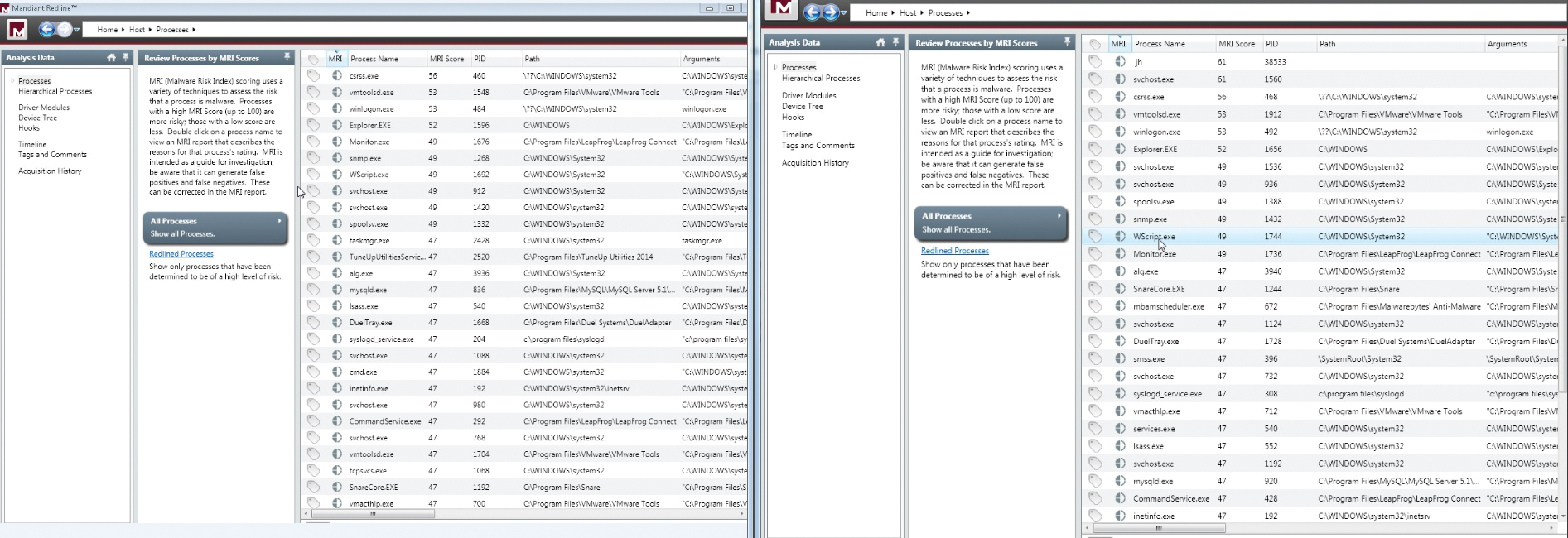
After comparing the two different lists, I see that, after reboot, new processes are running (jh MRI Score 61 PID 38533 and svchost.exe MRI Score 61 PID 1560). MRI (Malware Risk Index) is a score Redline uses to assess the likelihood that a process or artifact is associated with a malware event. Redline calculates the Malware Risk Index (MRI) score, which you can use to prioritize your investigation. The higher the MRI score, the more likely Redline has identified a potential compromise. You should inspect each process that is "redlined" (i.e., given a high MRI score) to determine the reasons Redline scored it as a threat. In this case, Redline didn't label the threat very high, but it is interesting that it is the highest scoring process, and it wasn't running before the malware was executed on the box. This process needs further investigation.
Conclusion
Every malware attack is different, and every investigation must follow a path based on the evidence, but that doesn't mean you can't bring your incidence response team together in advance and assemble the necessary tools, so you'll be ready in a crisis. In this article, I described some tools investigators use for obtaining and analyzing the memory of an infected system. In a later article, I will take a closer look at memory analysis tools such as Volatility and Mandiant Redline.
