
Desired State Configuration for Linux
Intercom
The central idea behind the Desired State Configuration (DSC) concept introduced in PowerShell 4 is that systems configure themselves relative to a desired state. The nodes to be managed either pull centralized scripts, or the desired settings are pushed to the nodes at defined intervals. The administrator can choose between push or pull mode. An SMB share or a web server can act as the distributor of the defined resources.
The large number of available resources for the filesystem, registry, server roles, and so on makes for useful deployment options in client and server administration. In a Windows environment, the required infrastructure is set up quickly. After installing the Windows Management Framework 4 [1], included in Server 2012 R2 and Windows 8.1, you already have the tools in place. PowerShell responds with version number 4.0 to $PSVersionTable, which means you have the required constructs for creating your own configurations: configuration, node, resource. Moreover, the Windows Remote Management (WinRM) service is up to date, which is a requirement for remotely controlling the target systems.
In other words, everything is set up for a homogeneous Windows environment – but what about Unix or Linux servers? Are the benefits of declarative administration ruled out? The good news is no, although you will need to do a little bit of preparatory work that you do not need to do on Windows. The heart of the system is the Open Management Infrastructure (OMI) stack, which was contributed by Microsoft to The Open Group for further development; it is an implementation of a standard by the Desktop (Distributed) Management Task Force, who developed a low-level layer in the form of Web-Based Enterprise Management (WBEM) for managing a variety of system indicators. Low-level requests still rely on this model to access BIOS information and hardware or network infrastructures. Even many PowerShell cmdlets, such as Get-Hotfix, encapsulate classes defined by this legacy standard.
Platform-independent availability makes OMI an obvious choice for tasks that go beyond the plain vanilla Windows universe. The Microsoft implementation relies on the Common Information Model (CIM) or Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI). DSC is just a minor element of the CIM family.
Requirements for PowerShell on Linux
The following components must exist for functional management of Unix/Linux in PowerShell:
- An appropriate data sink in the form of an OMI implementation for the system, because the requests from the management computer need to be transmitted to the target. The communications channel is the HTTP-based
WSManservice. The desired Linux implementation thus needs to be capable of processing requests via this channel. - A working DNS name resolution for Unix-based systems, because you use a script for management.
- An administrative target, because you control resources that are available on the Linux system.
- The central processing unit, the Local Configuration Manager (LCM), which processes the instructions stored in the configuration. At the same time, it offers the option of configuring the transmission type (Push, Pull).
- The computer in the
TrustedHostslist, because the Linux server is not a member of the domain. This list defines the clients to which Windows Server allows remote connections, but not the ones it accepts as incoming connections; you can easily handle this using PowerShell:
Set-Item WSMan:\localhost\client\TrustedHosts -value <IP of Linux Servers>
- An SSH server installed on the Linux computer.
The test setup looks like this: Windows Server 2012 R2 with DNS installed and configured; a CentOS 7 server as the target for the DSC script; SSH access successfully tested with name resolution using ping.
The HTTP listener, and thus the WinRM counterpart, is the Omiserver software package. Before you start the installation, you still need to make sure a few conditions are fulfilled. The C libraries for compiling the packages must be in place, as must a developer environment (python-dev).
For the test setup to work, the Omiserver and LCM sources, as well as the DSC resources, must reside in the same folder. Download the omiserver package [2]. After unpacking, follow the typical steps, configure, make, and make install. The installation is in opt/omi-1.0.8 by default; the executable resides in the bin subfolder. You can pick up the LCM and DSC resources as follows:
wget https://github.com/MSFTOSSMgmt/\ WPSDSCLinux/releases/download/v1.0.0-CTP/PSDSCLinux.tar.gz
For simplicity's sake, you will probably want to create a /DSC folder on the CentOS server. After unpacking in this directory, type make and make -reg. A call to
/opt/omi-1.0.8/bin/omiserver -d
should now work without any errors. At the same time, you will find the omicheck test script below /opt/omi-1.0.8/bin; this script will help in troubleshooting. If everything is configured correctly, you will see the output shown in Figure 1.
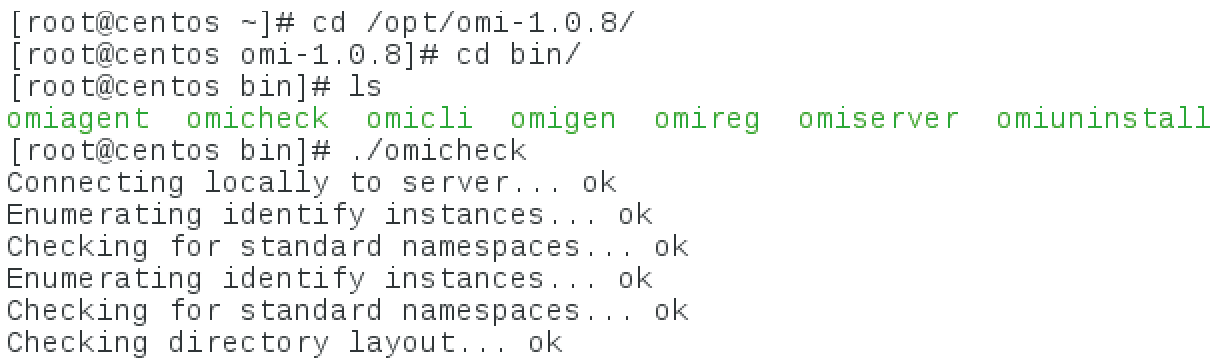
Microsoft's Add-Ons
Managing third-party operating systems is a crucial point for Microsoft in the development of PowerShell. If DSC is to be a key player in the future, it also needs to manage other operating systems skillfully.
Remote configuration based on DSC always consists of transferring a local CIM method to the remote instance. On a Windows system, DSC thus requires the same repositories to be installed on a management computer and target computer. A component specially developed for Linux needs to be provisioned on the Windows system to meet the same conditions. As you might expect, this component is a PowerShell module [3] that supplies the resources for Linux.
First, you need to unblock the file before extracting. Depending on the value currently set, ExecutionPolicy could prevent execution of the external script. After unpacking the folder and copying it into the PowerShell %systemroot%\system32\WindowsPower-Shell\v1.0\Modules directory, the new Linux/Unix resources it contains are then usable in DSC scripts. Check whether the output of the Get-Module -list command sees the nx module.
Test Run
Omiserver is ready to accept commands from Windows PowerShell. The connection is opened as a CIM session (CimSession). The difference between a regular PowerShell remote session (PSSession) and a CimSession is the type of possible return values. PSSessions are capable of transporting any PowerShell instruction. That is, they typically transport arbitrary .NET objects. In contrast, a CimSession only uses CIM/WMI objects.
However, this type of connection also offer some advantages. Low-level operating system functions are more typically mapped by CIM than .NET classes. Additionally, complex session management is unnecessary. After initializing the request on the target system and fielding the response, a CimSession automatically terminates. This lack of overhead makes this kind of remote connection attractive, given a large number of nodes.
The control unit I will be using is a resource of the nx module. The following command at the PowerShell console shows which resources are available (Table 1):
Get-DSCResource -name nx*
Tabelle 1: nx Module Resources
|
Name |
Process |
|---|---|
|
|
Create and delete folders and files; create content |
|
|
Group management |
|
|
Flexible resources for self-authored targets |
|
|
Start and stop services |
|
|
User management |
In a test run, I used the nxFile resource. The intent is to create a text file with content on the target computer as follows:
$Cred = Get-Credential -Username: "root" -Message: " Please use root"; $Opt = New-CimSessionOption -UseSSL:$True -SkipCACheck:$True \ -SkipCNCheck:$True -SkipRevocationCheck:$True;
Next, I define the login and transmission settings:
$LinuxServer = New-CimSession -Credential:$Cred \ -ComputerName: centos -Port:5986 -Authentication:Basic \ -SessionOp-tion:$Opt;
The connection to the Linux server is opened using the hostname. The next step is to specify the HTTP(S) port and authentication method. An nxFile section in the script defines what exactly happens during the call (Listing 1).
Listing 1: DSC Script for Linux
01 Configuration Centos_File
02 {
03 Import-DSCResource -Module nx
04 Node $LinuxServer.ComputerName
05 {
06 nxFile file
07 {
08 DestinationPath ="/tmp/test"
09 Contents="Hello Linux and DSC"
10 Ensure="Present"
11 Type="File"
12 }
13 }
14 }
15 Write-Host " Executing configuration ..";
16 Centos_File -OutputPath C:\udat\LinuxConfigs\ | Out-Null ;
A Managed Object File (MOF), which is the control unit for a DSC application, has now been created below C:\udat\LinuxConfigs, where you will find all the required information, such as the TargetNode, Resource, and so on. If you want to configure multiple nodes, a MOF is created for each target. The following call starts DSC:
Start-DscConfiguration -CimSession:$LinuxServer \ -Path:"C:\udat\LinuxConfigs" -Verbose -Wait ;
With the -Verbose parameter set, I can monitor the action. If no problems occur, the output will look like Figure 2. The classes used are shown, along with their methods, and no errors were reported. However, I still don't know whether the instructions really have any effect on the target system. A quick check of the Unix filesystem shows that the action was successful (Figure 3).
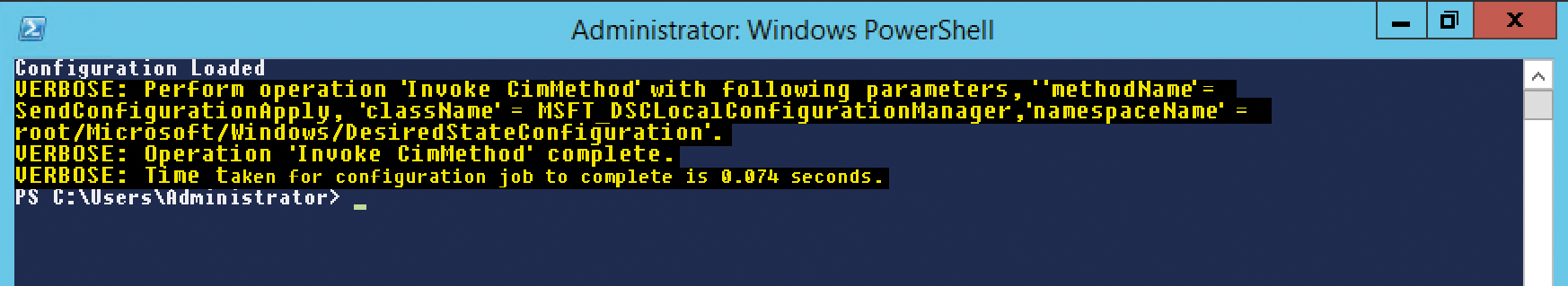
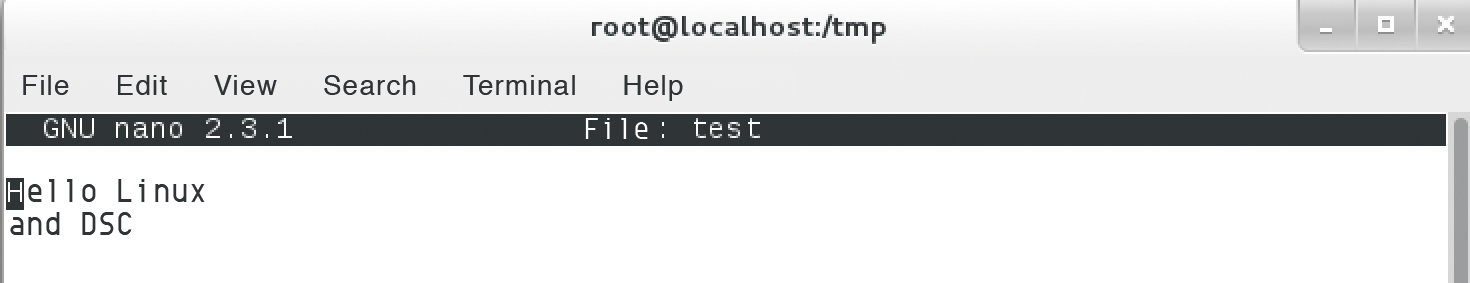
You can now make liberal use of the capabilities offered by the nx module. If you are interested in user management you can type
Get-DscResource -Name nxUser | Select \ -ExpandProperty Properties
to explore the nxUser resource's capabilities, and you can use the same approach for all the other elements.
Conclusions
The "declarative instead of imperative" approach certainly has its charm on Windows servers. Instead of an admin testing a setting manually and adjusting it as needed, the systems pick up the desired settings autonomously. Because an open standard was chosen to achieve this objective, DSC becomes future proof. OMI implementations are available for Linux, Apple, and Android, so nothing can prevent you from defining a universal configuration. The only thing left to be desired is an infrastructure that facilitates the process of creating nodes and assigned resources.
