
Working with objects in PowerShell
Useful Tool
If you want to professionally manage Windows systems, and above all servers, it's hard to avoid using PowerShell. Many admins, however, find it somewhat difficult to cope with the object-oriented approaches of the scripting language. Our workshop provides assistance and illuminates the fundamental concepts.
Of course, admins use scripting languages to handle administrative and support tasks, and many system administrators will have had no alternative but to delve the depths of the SQL language. Basically, most administrators want to do their jobs rather than develop programs, which explains why many experienced Windows admins have a certain aversion to working with PowerShell. This is particularly unfortunate, because this language can significantly facilitate the work, specifically because of its structure and object-oriented approach (see the "Object-Oriented Structure in PowerShell" box for more information). The motivation behind this article is thus to show how the developers implemented this concept and how the scripting language uses these objects.
Working with Objects
If you want to work with the data of an object, you need to call its members. These are the components that let you access and edit the information. A PowerShell object supports a whole range of members, the most famous examples being properties and methods. When you work with objects, you use the methods to perform actions, and the properties, to access information. An object's properties include, for example, values such as the file size or the date on which the file was created, whereas deleting or moving the file is one of the methods provided by the respective object.
If you want to learn and understand more about the concepts and capabilities of PowerShell, your best bet – as with any scripting and programming language – is to try the examples yourself. One of the PowerShell cmdlets that people like to use for this purpose is Get-Service. It outputs a list of the services installed on a computer. If called without any parameters, the cmdlet also outputs details about the services on the local system.
Each service that is returned by the Get-Service cmdlet is an object based on the .NET System.ServiceProcess.ServiceController class. Of course, the ServiceController object also includes a number of properties and methods that a user can draw on to access the data in the object or perform operations against the data. They include, for example, the properties of the name and the DisplayName of the system service. The value associated with the properties of DisplayName is the display name of the service. The ServiceController object also provides a number of methods: You can use the Start method to start the service represented by the object and the Stop method to stop it again.
It is unlikely that an admin could memorize all the properties, methods, or even member types of the objects to access and use them correctly. PowerShell thus provides a tool that helps you retrieve detailed information about the respective members of an object: the Get-Member cmdlet. If you want to know, for example, which members the get-service cmdlet provides, you can retrieve this information by typing:
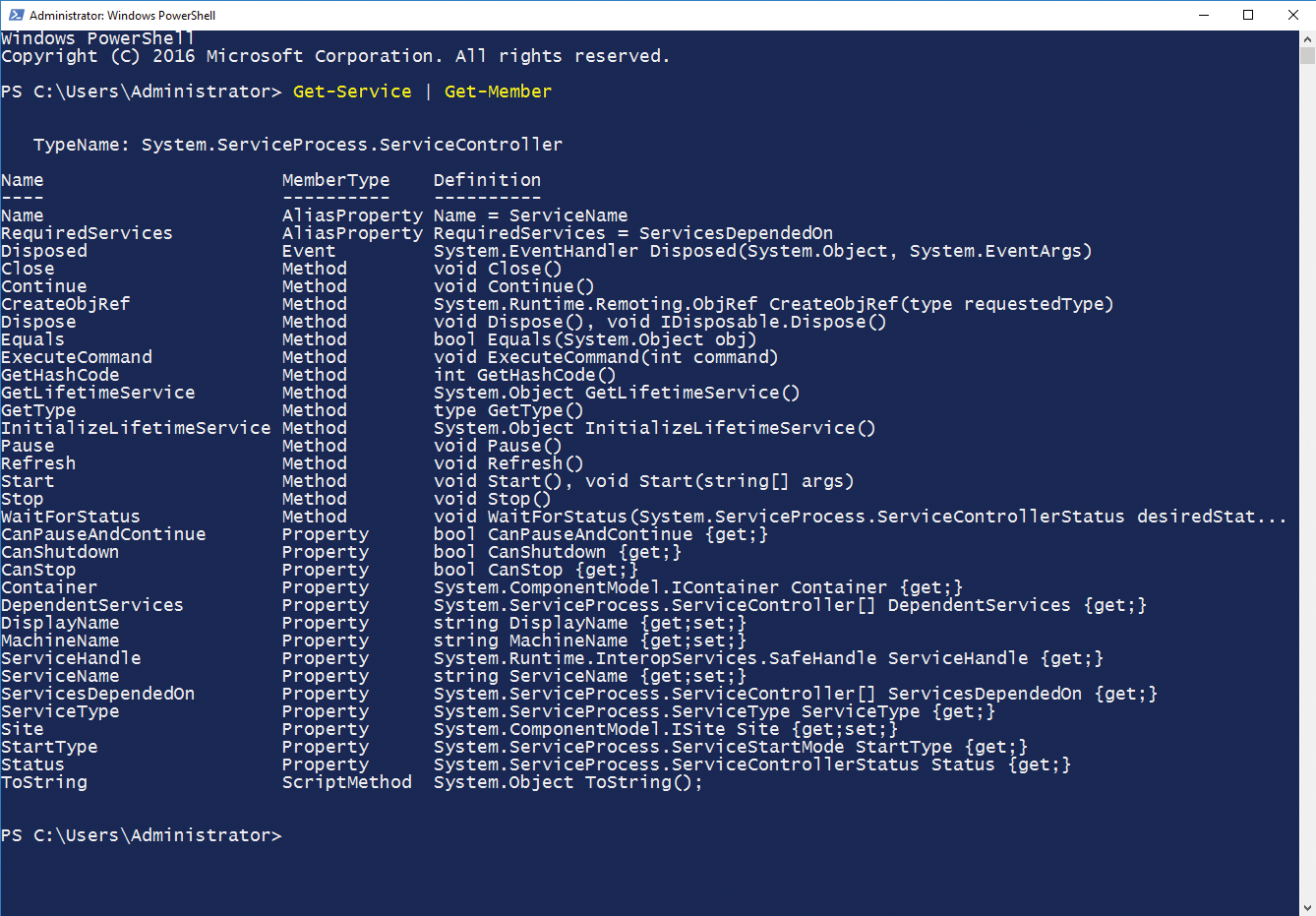
> Get-Service | Get-Member
The objects that Get-Service returns are piped (as represented by the | character) to the input of the Get-Member cmdlet (Figure 1). The following output shows what members, methods, and properties a cmdlet provides. The list includes the name of each member, its type, and a definition. To what extent this definition is useful for you, depends to a large extent on your programming skills. In any case, you can determine in this way that Service.Controller comes with a whole bunch of members and also see their names. Also, this example shows very nicely that these are mostly methods and properties of the respective object.
Detailed Information on Objects
For users, who are already familiar with the .NET classes, this output is worth a closer look. It first displays the type name of the class on which this object is based – in this case, System.ServiceProcess.ServiceController. There is another, very interesting aspect to this information: Inspection of the results returned by Get-Member shows that they only include the details of a single object, even though the Get-Service cmdlet returns an object for each service. The reason for this is the way the Get-Member cmdlet works. If it notes that several objects of the same type are returned, it only shows you one instance of these objects in the output. The developers did this to avoid redundancies. The cmdlet only returns the class on which all these objects are based.
If the command does not return more than one object type, Get-Member displays the appropriate information for each of these types. An example of this is calling the Get-ChildItem cmdlet for a directory that includes both files and subdirectories (Figure 2):
> Get-ChildItem H:\tmp | Get-Member
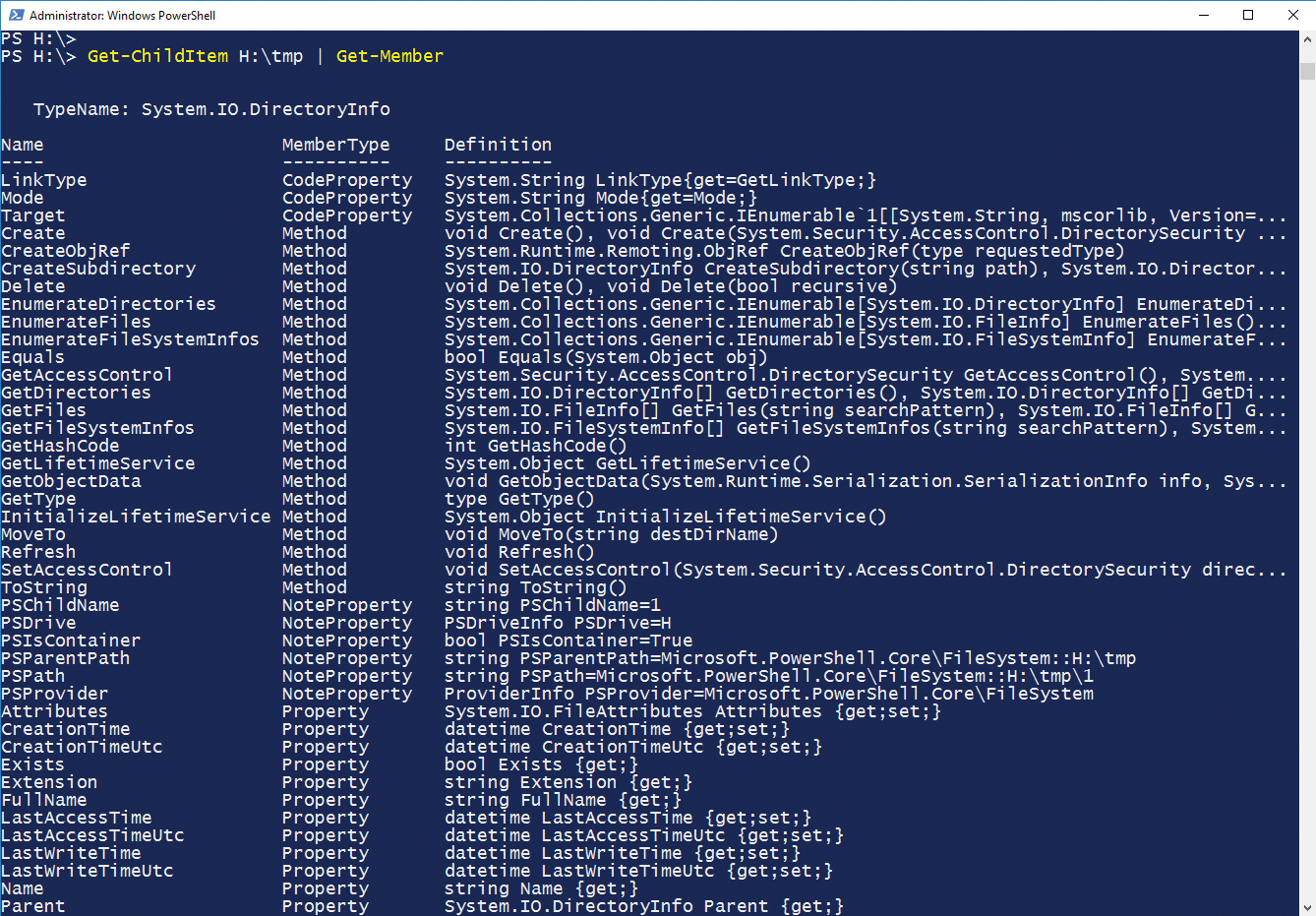
Get-Member now displays details of the classes System.IO.DirectoryInfo (for directories) and System.IO.FileInfo (for the files in the directory H:\tmp). If this directory only contained directories, Get-Member would display only the details of System.IO.DirectoryInfo. Users who want to use Get-Member thus need to ensure that they actually get to see the object types that they are really interested in.
Get-Member has still more to offer: For example, the user can display a list, consisting of a special member type, such as the properties or the methods. If you need this kind of output, you need to add the -MemberTyp parameter followed by the name of the desired type in the call. The following call ensures that only the properties of the respective object are displayed on the screen:
> Get-Service | Get-Member -MemberTyp Property
The ability to specifically request such details makes it easier to access the information within an object. It does not matter whether you are interested in a specific member or a whole list of the members of an object.
Even More Targeted and Detailed
For example, if you already know that the ServiceController class supports the properties Status and ServiceTyp, you can use this information in a targeted way to specify your own commands and their output. For example, the following command uses these properties together with the Where-Object cmdlet to filter the results as desired:
> Get-Service | Where {$_.Status -eq "Running" `-and $_.ServiceType -eq "Win32OwnProcess"}
Again Get-Service returns a set of ServiceController objects that are then routed through the pipe to the Where-Object cmdlet. I used the Where alias for this cmdlet. For each of the objects passed to the Where-Object cmdlet, you can now access its properties to develop the desired filter. This is why you need to use the $_ symbol. This is a system variable that always points to the current object in the pipeline, which makes it particularly well suited to processing these objects in sequence. This symbol must be followed by a dot, in turn followed by the name of the property; I selected the Status property here.
You can now use this to return specific data in line with your specifications. To do this, you can use Boolean expressions, which determine whether this information is true or false. In this case, I first stipulated that the Status property must have a value of Running and that the ServiceTyp property must be equal to the value of Win32-OwnProcess.
In both cases, the -eq (for "equals") operator is used. With its help, you can determine whether the required values apply. The -and operator is added to link the two expressions. Based on Boolean logic, both expressions must be "true" and the properties must contain the required value for an object to be returned. An important note about this example: The ` character at the end of the first line tells the PowerShell interpreter to continue the code on the next line. If this is missing, the PowerShell command ends at the end of the line, and you will see an error message.
This is a good example of a user's access to the information that they were originally looking for being facilitated by knowing the names of the properties that are supported by the respective object. If you want to take this example a step further, you can pass the results of the command to the Format-Table cmdlet:
> Get-Service | Where {$_.Status -eq "Running" `-and $_.ServiceType -eq "Win32OwnProcess"} | `Format-Table -Autosize
This again demonstrates the power of the pipeline mechanism.
Processing Data Downstream
When users start to deal with the properties and capabilities of objects in more detail, newcomers may gain the impression that PowerShell's object-oriented approach is a nice solution but hardly offers any practical advantages in comparison with the type of legacy shell programming that they may be familiar with from Linux/Unix systems. To illustrate the difference and the advantages, it is important to remember how information is displayed in the Bash shell, for example. A purely text-oriented program like IPconfig (or ifconfig on Linux derivatives) outputs all its results as plain text.
If you want to access or continue to use only on certain values from this output, you need to turn to filter programs like awk, grep, or sed. PowerShell offers a cmdlet Get-NetIPConfiguration that basically outputs the same data (Figure 3). But because objects are output here, the user can directly access the members. The following call gives you an example of this:
> (Get-NetIPConfiguration).DNSServer
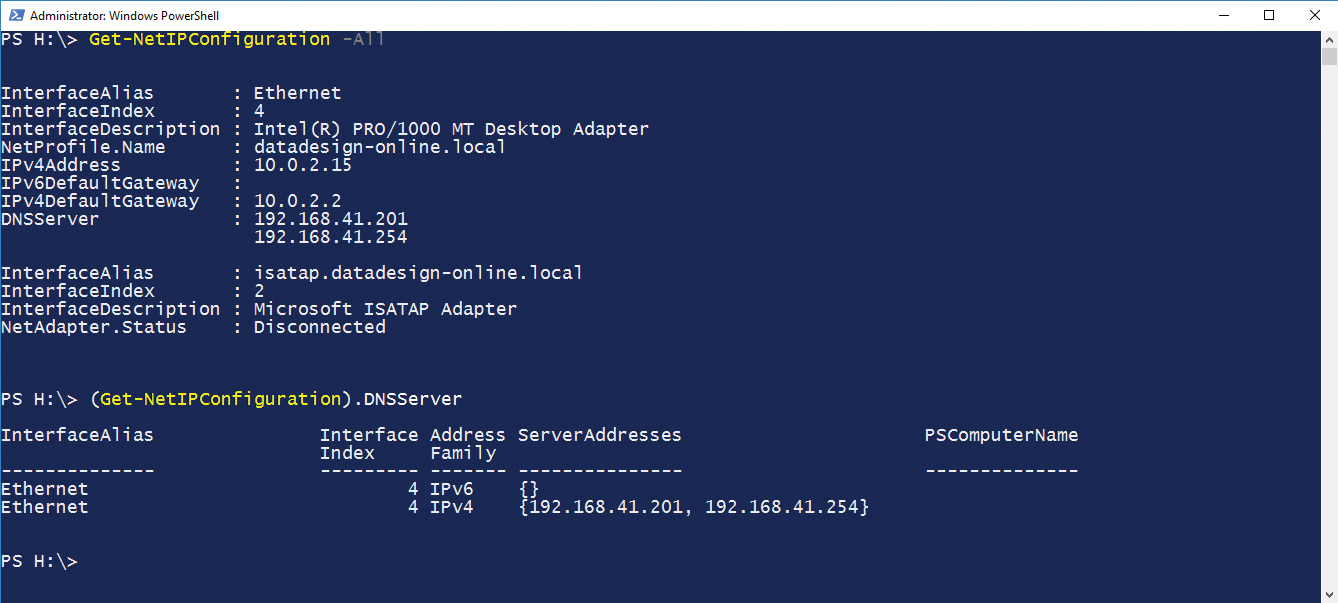
Get-NetIPConfiguration cmdlet may output the same information as the ipconfig command line, but the user can specifically access the desired property, which contains a desired piece of information, here.This only outputs the data for the DNS server configured on this computer. The type of call is particularly important here: The Get-NetIPConfiguration cmdlet must be enclosed in brackets. Otherwise, PowerShell interprets the call as a complete name of the format Get-NetIPConfiguration.DNSServer and outputs an error message, saying that it can't find any such command. Use of the brackets tells the PowerShell interpreter to first run the command within the bracket and generate a ServiceController object. PowerShell then directly accesses the properties of the DNSServer property and displays them.
This type of access works well if you only need the status of a particular process on your system for further processing in a script, for example. The following command
> (Get-Service - Name Teamviewer).Status
tells the cmdlet to display only the "Running" output if the TeamViewer service is active on the system.
Conclusions
Take a good look at the objects, their members, properties, and methods with the help of the Get-Member cmdlet and experiment with the different access options and capabilities – you will soon see how many opportunities you have to put them into practice for fast and efficient scripting.
